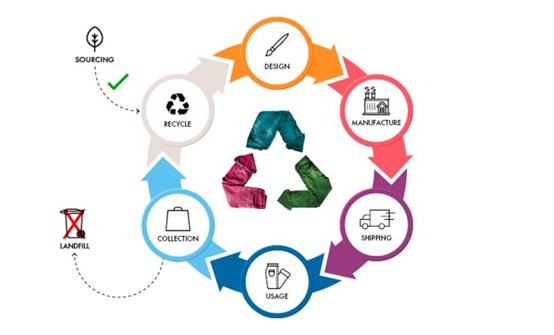
Sustainable fashion has become a common topic and vane in the international industry and fashion circles. As one of the most polluted industries in the world, how to build an eco-friendly sustainable system through sustainable design, production, manufacturing, consumption, and reuse of fashion industry is an important development direction of fashion in the future. Do you really understand these 9 sustainable terms for the fashion industry?
1. Sustainable Fashion
Sustainable fashion is defined as follows: it is the behavior and process that promotes the transformation of fashion products and fashion systems to more ecological integrity and more social justice.
Sustainable fashion is not just about fashion textiles or products, but also about the entire fashion system, which means that the interdependent social, cultural, ecological, and even financial systems are involved. Sustainable fashion needs to be considered from the perspective of many stakeholders, such as consumers, producers, all biological species, present and future generations, etc.
Sustainable Fashion’s goal is to create a stronger ecosystem and community through its actions. These actions include enhancing the value of industries and products, extending the life cycle of materials, increasing the service life of clothing, reducing the amount of waste and pollution, and reducing the harm to the environment during production and consumption. It also aims to educate the public to practice more ecologically friendly consumption by promoting “green consumers”.
2. Circular Design
Circular design refers to a closed chain in which resources in the design process can be continuously reused in different forms instead of being wasted.
Circular design requires improved raw material selection and product design, including the use of standardized and modular ingredients, the use of purer materials and easier decomposition. It also requires an innovative design process, and therefore the selection of effective design strategies, concepts, and tools. Circular design also requires attention to all aspects of reuse, from products to materials, production processes and conditions, so a complete system and a deep understanding of ecology are essential.
Circular design means that the resources in the design process can be continuously reused in different form.
3. Biodegradable Materials
Biodegradable materials are those that, under the right conditions and in the presence of microorganisms, fungi, and bacteria, will eventually be broken down into their original components and incorporated into the soil. Ideally, these substances will break down without leaving any toxins. For example, when a plant product is eventually broken down into carbon dioxide, water, and other natural minerals, it blends seamlessly into the soil. However, many substances, even those labeled as biodegradable, break down in a more harmful way, leaving chemical or destructive substances in the soil.
Obvious biodegradable materials include food, un-chemically treated wood, etc. Others include paper products, etc. Such as steel and plastics, are biodegradable but take years.
Biodegradable materials also include bioplastics, bamboo, sand and wood products.
Click the link to search our biodegradable materials. https://www.colorpglobal.com/sustainability/
4. Transparency
Transparency in the fashion industry includes fair trade, fair salary, gender equality, corporate responsibility, sustainable development, good working environment and other aspects of information openness. Transparency requires companies to let consumers and investors know who is working for them and under what conditions.
Specifically, it can be divided into the following points: First, the brand needs to disclose its manufacturers and suppliers, reaching the level of raw materials; Make public the contact information of the company’s sustainable development, corporate responsibility, and other relevant departments; Analyze more data on carbon emissions, water consumption, pollution and waste production; Finally, responding to consumer-related questions is not just about fulfilling duties or obligations.
5. Alternative Fabrics
Alternative fabrics refer to reducing reliance on cotton and focusing on more sustainable fabric options. Common alternative fabrics are: bamboo, organic cotton, industrial hemp, renewable polyester, soy silk, organic wool, etc. For example, a quarter of the world’s pesticides are used in the production of conventional cotton, while organic cotton is grown in a non-toxic environment with no synthetic chemical inputs, which reduces environmental pollution during production.
It is worth noting that even the use of alternative fabrics cannot completely eliminate the environmental impact. In terms of energy, toxins, natural resources and water consumption, the production of clothing has a certain impact on the environment.
6. Vegan Fashion
Clothing that does not contain any animal products is called vegan fashion. As consumers, it is important to pay attention to the material of clothing. By checking the label, you can determine if the garment contains non-textile ingredients such as animal ingredients, and if so, it is not a vegan product.
Common animal products are: leather products, fur, wool, cashmere, Angora rabbit hair, Angora goat hair, goose down, duck down, silk, sheep horn, pearl shellfish and so on. Common pure materials can be divided into degradable materials and non-degradable materials. Degradable natural fibers include cotton, oak bark, hemp, flax, Lyocell, bean silk, artificial fiber, etc. Non-degradable synthetic fiber category: acrylic fiber, artificial fur, artificial leather, polyester fiber, etc.
7. Zero-waste Fashion
Zero waste fashion refers to fashion that produces none or very little fabric waste. To achieve zero waste can be divided into two methods: zero waste fashion before consumption, can reduce waste in the production process; Zero waste after consumption, through the use of second-hand clothing and other ways to reduce the waste in the middle and late clothing cycle.
Zero-waste fashion before consumption can be achieved by optimizing the pattern-making process in clothing production or reusing discarded materials in tailoring. Zero-waste fashion after consumption can be achieved by recycling and Upcycling clothes, transforming old clothes into different effects.
8. Carbon Neutral
Carbon neutral, or achieving a zero-carbon footprint, refers to achieving net zero carbon dioxide emissions. There are direct and indirect carbon emissions. Direct carbon emissions include pollution from production processes and resources directly owned by enterprises, while indirect emissions include all emissions from the use and purchase of goods.
There are two ways to achieve carbon neutrality: one is to balance carbon emissions and carbon elimination, and the other is to completely eliminate carbon emissions. In the first approach, carbon balance is usually achieved through carbon offsets, or offsetting emissions by transferring and sequestering carbon dioxide from the environment. Some carbon-neutral fuels do this by natural or artificial means. The second approach is to change the energy source and the production process of the enterprise, such as switching to renewable energy sources such as wind or solar.
9. Ethical Fashion
Ethical fashion is a term used to describe an ethical fashion design, production, retail and purchasing process that includes a range of factors such as working conditions, labor, fair trading, sustainable production, environmental protection, and animal welfare.
Ethical Fashion aims to address the current issues facing the fashion industry, such as labor exploitation, environmental damage, use of toxic chemicals, waste of resources and animal injury. For example, child labor is one type of labor that can be considered exploited. They face forced long hours, unsanitary working conditions, food, and low pay. Lower fast fashion prices mean less money is being paid to workers.
As a label and packaging enterprise in the garment industry, COLOR-P follows the footsteps of our customers, implements sustainable development strategies, assumes corporate social responsibility, and makes real efforts to achieve a transparent supply chain for customers. If you are looking for a sustainable labeling and packaging option, we would be your reliable partner.
Post time: Jun-28-2022